Molecular imaging of Cathepsin E-positive tumors in mice using a novel protease-activatable fluorescent probe†
Abstract
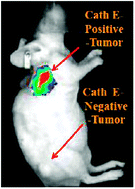
The purpose of this study is to demonstrate the ability of imaging Cathepsin E (Cath E) positive tumors in living animals through selective targeting of Cath E proteolytic activity using a sensitive molecular imaging agent. Methods: a

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...