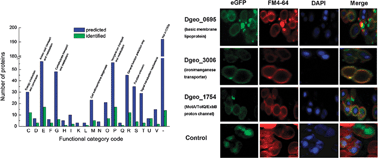
Deinococcus geothermalis is a radioresistant and moderate thermophilic bacterium. Little was known about the membrane or membrane associated proteins of this bacterium. This study established the membrane subproteome profile of D. geothermalis, using 1-D PAGE and LC-MS/MS analysis following Triton X-114 detergent extraction. A total of 552 proteins from the membrane preparations were identified from two independent trials. In the total identified proteins, 117 were membrane subproteomic proteins, and 89 of them were described for the first time in D. geothermalis including fimbrial pilin (Dgeo_2038), cytochrome bd ubiquinol oxidase (Dgeo_2705) and multi-sensor (Dgeo_2096). The major membrane subproteomic proteins were distributed into 18 functional groups including nutrient transport and metabolism, energy production and conversion, cell wall/membrane biogenesis and a poorly characterized subclass. The identifications of Deinococcus-specific proteins, such as cell surface receptor IPT/TIG (Dgeo_1119) and four hypothetical proteins, demonstrated the special protein composition and functions in the cell membrane of Deinococcus. The results provide a basis for quantitative proteomic analysis, which will facilitate the understanding of the adaptation of this organism to different environmental stresses and the development of strategies for bioremediation of environmental waste.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...