Conformational averaging in structural biology: issues, challenges and computational solutions†
Abstract
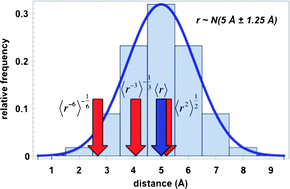
Most experimental methods in structural biology provide time- and ensemble-averaged signals and, consequently, molecular structures based on such signals often exhibit only idealized, average features. Second, most experimental signals are only indirectly related to real, molecular geometries, and solving a structure typically involves a complicated procedure, which may not always result in a unique solution. To what extent do such conformationally-averaged, non-linear experimental signals and structural models derived from them accurately represent the underlying microscopic reality? Are there some structural motifs that are actually artificially more likely to be “seen” in an experiment simply due to the averaging artifact? Finally, what are the practical consequences of ignoring the averaging effects when it comes to functional and mechanistic implications that we try to glean from experimentally-based structural models? In this review, we critically address the work that has been aimed at studying such questions. We summarize the details of experimental methods typically used in structural biology (most notably nuclear magnetic resonance,
- This article is part of the themed collection: Computational and systems biology

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...