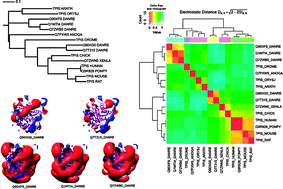
The electrostatic potential of an enzyme is a key determinant of its substrate interactions and catalytic turnover. Here we invoke comparative analysis of protein electrostatic potentials, along with sequence and structural analysis, to classify and characterize all the enzymes in an entire pathway across a set of different organisms. The electrostatic potentials of the enzymes from the glycolytic pathway of 11 eukaryotes were analyzed by qPIPSA (quantitative protein interaction property similarity analysis). The comparison allows the functional assignment of neuron-specific isoforms of triosephosphate isomerase from zebrafish, the identification of unusual protein surface interaction properties of the mosquito glucose-6-phosphate isomerase and the functional annotation of ATP-dependent phosphofructokinasesand cofactor-dependent phosphoglycerate mutases from plants. We here show that plants possess two parallel pathways to convert glucose. One is similar to glycolysis in humans, the other is specialized to let plants adapt to their environmental conditions. We use differences in electrostatic potentials to estimate kinetic parameters for the triosephosphate isomerases from nine species for which published parameters are not available. Along the core glycolytic pathway, phosphoglycerate mutase displays the most conserved electrostatic potential. The largest cross-species variations are found for glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, enolase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. The extent of conservation of electrostatic potentials along the pathway is consistent with the absence of a single rate-limiting step in glycolysis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...