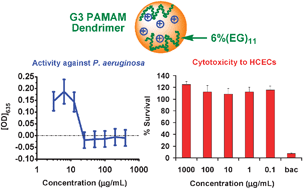
We have investigated the antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of a series of amino-terminated poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers modified with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) groups. The antibacterial activity of the PAMAM dendrimers and their derivatives against the common ocular pathogens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, was evaluated by their minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). For the unmodified third and fifth generation (G3 and G5) amino-terminated dendrimers, the MICs against both P. aeruginosa and S. aureus were in the range of 6.3–12.5 μg mL−1, comparable to that of the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 (1.3–12.5 μg mL−1) and within the wide range of 0.047–128 μg mL−1 for the fluoroquinolone antibiotics. PEGylation of the dendrimers decreased their antibacterial activities, especially for the Gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus). The reduction in potency is likely due to the decrease in the number of protonated amino groups and shielding of the positive charges by the PEG chains, thus decreasing the electrostatic interactions of the dendrimers with the negatively-charged bacterial surface. Interestingly, localization of a greater number of amino groups on G5 vs. G3 dendrimers did not improve the potency. Significantly, even a low degree of PEGylation, e.g. 6% with EG11 on G3 dendrimer, greatly reduced the cytotoxicity towards human corneal epithelial cells while maintaining a high potency against P. aeruginosa. The cytotoxicity of the PEGylated dendrimers to host cells is much lower than that reported for antimicrobial peptides. Furthermore, the MICs of these dendrimers against P. aeruginosa are more than two orders of magnitude lower than other antimicrobial polymers reported to date. These results motivate further exploration of the potential of cationic dendrimers as a new class of antimicrobial agents that may be less likely to induce bacterial resistance than standard antibiotics.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...