Combined potentiometric, calorimetric and spectroscopic methods were used to investigate the Cu2+ binding ability and coordination behaviour of some peptide fragments related to the neurotoxic region of chicken Prion Protein. The systems studied were the following protein fragments: chPrP106–114, chPrP119–126, chPrP108–127, chPrP105–127 and chPrP105–133.
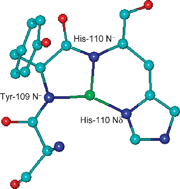
The complex formation always starts around pH 4 with the coordination of an imidazole nitrogen, followed by the deprotonation and binding of amide nitrogens from the peptidic backbone. At neutral pH, the {Nim, 3N−} binding mode is the preferred one. The amide nitrogens participating in the binding to the Cu2+ ion derive from residues from the N-terminus side, with the formation of a six-membered chelate ring with the imidazolic side chain.
Comparison of thermodynamic data for the two histydyl binding domains (around His-110 and His-124), clearly indicates that the closest to the hexarepeat domain (His-110) has the highest ability to bind Cu2+ ions, although both of them have the same coordination mode. Conversely, in the case of the human neurotoxic peptide region, between the two binding sites, located at His-96 and His-111, the farthest from the tandem repeat region is the strongest one. Finally, thermodynamic data show that chicken peptide is a distinctly better ligand for coordination of copper ions with respect to the human fragment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...