A colorimetric sensing platform based on self-assembled 3D porous CeGONR nanozymes for label-free visual detection of organophosphate pesticides†
Abstract
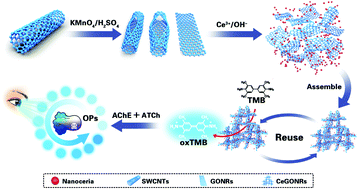
Analytical methods for detecting organophosphorus pesticides (OPs) with high sensitivity as well as on-site screening are urgently required to guarantee food safety and protect ecosystems. Herein, we developed a Ce(III)-driven self-assembled strategy to fabricate nanocomposites (CeGONRs) by a facile method. We used multiple characterization techniques and revealed that CeGONRs form a 3D porous structure and possess high surface-to-volume ratios, mixed valence, and multiple catalytic sites. We have also demonstrated that high-performance CeGONRs have nanozyme catalytic ability and revealed their synergistic catalytic mechanism. As a proof of concept, we investigated the excellent catalytic property of the CeGONRs by catalyzing the oxidation of a 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) substrate to produce a blue color. Furthermore, based on the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) enzyme inhibition method, upon the addition of AChE and acetylthiocholine (ATCh), the blue becomes colorless; OPs inhibited the activity of AChE, and prevented the generation of thiocholine (TCh), accompanied by no color change. The CeGONR nanozyme-based sensing platform was used successfully for the colorimetric detection of OPs. OPs were detected at 3.43 ng mL−1 (0.0034 ppb) and the linear range was from 0.012 to 3.50 μg mL−1. The corresponding LOD for chlorpyrifos was measured to be lower than 2 ppb that is below the maximum residue limit (MRL) adopted by the national food safety standard of China. The color change was observable by the naked eye and successfully applied to paper-based disposable test strip screening for OPs; satisfactory results were also obtained using cabbage samples. The rational design of CeGONRs sheds light on the catalytic mechanism and provides a versatile approach for constructing artificial enzymes that can be potentially used for a rapid, on-site, paper-based visual screening of a large number of samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...