Enrichment of rare events using a multi-parameter high throughput microfluidic droplet sorter†
Abstract
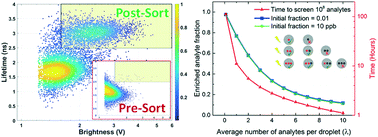
High information content analysis, enrichment, and selection of rare events from a large population are of great importance in biological and biomedical research. The fluorescence lifetime of a fluorophore, a photophysical property which is independent of and complementary to fluorescence intensity, has been incorporated into various imaging and sensing techniques through microscopy, flow cytometry and droplet microfluidics. However, the throughput of fluorescence lifetime activated droplet sorting is orders of magnitude lower than that of fluorescence activated cell sorting, making it unattractive for applications such as directed evolution of enzymes, despite its highly effective compartmentalization of library members. We developed a microfluidic sorter capable of selecting fluorophores based on fluorescence lifetime and brightness at two excitation and emission colors at a maximum droplet rate of 2.5 kHz. We also present a novel selection strategy for efficiently analyzing and/or enriching rare fluorescent members from a large population which capitalizes on the Poisson distribution of analyte encapsulation into droplets. The effectiveness of the droplet sorter and the new selection strategy are demonstrated by enriching rare populations from a ∼108-member site-directed mutagenesis library of fluorescent proteins expressed in bacteria. This selection strategy can in principle be employed on many droplet sorting platforms, and thus can potentially impact broad areas of science where analysis and enrichment of rare events is needed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
