Automated microchannel alignment using innate opto-signature for microchip electrophoresis†
Abstract
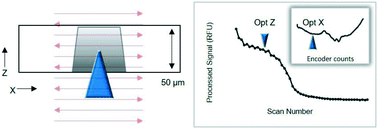
In laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) detection, optimal alignment is essential in maximizing the fluorescent signal and, hence, detection sensitivity. Micro-total analysis systems (μTAS) involving microchip electrophoresis (ME) are challenged with alignment of the optics to the separation channel each run due to the single-use nature. Furthermore, μTAS devices that are designed to operate autonomously and by non-experts face additional challenges in performing alignment with micrometer resolution without human intervention. As part of the development of a total DNA analysis system, we set out to develop an automated alignment (AA) method to locate a 50-by-50 μm separation channel on a freely rotating microfluidic device in the absence of a fluorescent dye, accomplished without additional hardware. We detail the innate fluorescent signature attainable from laser excitation and the optimization of the algorithm to achieve AA at 84.6% success rate from 26 microchips. This AA method was a key element in realizing complete automation of the DNA analysis process in order to advance our instrument to a technology readiness level of 7. This is the first description of an AA method for ME (and centrifugal ME) with the purpose of providing transparent technical details to bridge the gap from ‘fully integrated’ to ‘fully automated’ instruments for point-of-detection, sample in-answer-out use cases. Written in the context of a forensic application, the AA method is adaptable for a wide range of bioanalytical applications involving LIF detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
