Tri-fluid mixing in a microchannel for nanoparticle synthesis†
Abstract
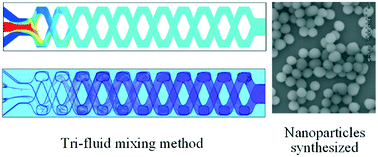
It is becoming more difficult to use bulk mixing and bi-fluid micromixing in multi-step continuous-flow reactions, multicomponent reactions, and nanoparticle synthesis because they typically involve multiple reactants. To date, most micromixing studies, both passive and active, have focused on how to efficiently mix two fluids, while micromixing of three or more fluids together (multi-fluid mixing) has been rarely explored. This study is the first on tri-fluid mixing in microchannels. We investigated tri-fluid mixing in three microchannel models: a straight channel, a classical staggered herringbone mixing (SHM) channel, and a three-dimensional (3D) X-crossing microchannel. Numerical simulations and experiments were jointly conducted. A two-step experimental process was performed to determine the tri-fluid mixing efficiencies of these microchannels. We found that the SHM cannot significantly enhance mixing of three streams especially for a Reynolds number (Re) higher than 10. However, the 3D X-crossing channel based on splitting-and-recombination (SAR) showed effective tri-mixing performance over a wide Re range up to 275 (with a corresponding flow rate of 1972.5 μL min−1), thereby enabling high microchannel throughput. Furthermore, this tri-fluid micromixing process was used to synthesize a kind of Si-based nanoparticle. This achieved a narrower particle size distribution than traditional bulk mixing. Therefore, SAR-based tri-fluid mixing is an alternative for chemical and biochemical reactions where three reactants need to be mixed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...