Condensing-enriched magnetic photonic barcodes on superhydrophobic surface for ultrasensitive multiple detection†
Abstract
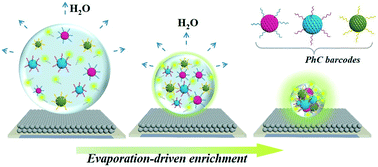
The ultrasensitive detection of multiple nucleic acids has great significance in a broad range of medical fields since nucleic acid samples are usually of small volumes and highly diluted. Herein, we present a novel magnetic photonic crystal (PhC) barcode-integrated condensing-enriched superhydrophobic platform for the ultrasensitive multiple miRNA detection. Droplets containing targets could suck the hydrogel PhC barcodes without losing their targets due to the difference in wettability between the hydrophilic PhC barcodes and hydrophobic substrate. During the evaporation of water from the droplet microreactors, these targets could be effectively enriched in the barcodes for achieving higher sensitivities. As the encoding signals of the PhC barcodes are the characteristic reflection peaks generated by their ordered physical nanostructures, the barcodes are stable and free from any fluorescent background and photobleaching; thus, they are accurate for distinguishing different targets. In addition, with the integration of magnetic nanoparticles into the hydrogel PhC barcodes, they could be imparted with the features of immobilization during change of medium and flexible movement for controlling the reaction, both of which could facilitate the detection processes. Based on this platform, we have demonstrated that the detection limit of multiple miRNAs is improved by about three orders. Thus, our platform is an ideal alternative for the ultrasensitive simultaneous multiplex analysis in medical fields.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Lab on a Chip Recent HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...