A microfluidic sensor for detecting chlorophenols using cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs)
Abstract
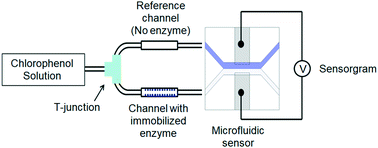
Chlorophenols have a strong medicinal smell and can be detected by the human nose at parts-per-million levels. Therefore, continuous monitoring of chlorophenols in water supplies is highly important. Herein, we reported a microfluidic sensor which can be used to detect 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) in real time with a limit of detection of around 0.1 ppm. The microfluidic sensor is a membrane-less galvanic cell which consists of two laminar flows running in parallel inside a straight channel. The sensor measures the potential difference between a solution containing 2,4-DCP and a reference solution containing acetate buffer. In a continuous-flow mode, the cell potential is proportional to the concentration of 2,4-DCP. To render specificity for the sensor, we incorporate a pre-treatment section where the incoming solution containing 2,4-DCP is split into two streams. One of the streams is brought into contact with cross-linked laccase aggregates (which catalyzes the hydrolysis of 2,4-DCP) and the second stream is taken as a reference solution. By comparing the potential difference between the two streams, we can determine the concentration of 2,4-DCP with high specificity. The microfluidic sensor platform is potentially useful for real-time detection of micropollutants present in aquatic systems with high sensitivity and specificity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...