Sensitive and rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria from urine samples using multiplex recombinase polymerase amplification†
Abstract
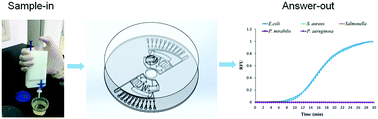
Bacterial infections may cause severe diseases such as tuberculosis, sepsis, nephritis and cystitis. The rapid and sensitive detection of bacteria is a prerequisite for the treatment of these diseases. The current gold standard for bacterial identification is bacteriological culture. However, culture-based identification takes 3–7 days, which is time-consuming and laborious. In this study, bacteria in urine samples were enriched using a portable filter-based pipette. Then, a centrifugal chip was constructed to detect multiple pathogenic bacteria from urine samples by integrating the DNA extraction, multiplex recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) and fluorescent detection together. This eliminated the time-consuming cultivation step, and thus accelerated the diagnosis of the urinary tract infections (UTIs). The five major pathogenic bacteria in UTIs were detected in this study, which are Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella typhimurium. Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus were successfully detected with limits of detection of 100 CFU mL−1 from urine samples within 40 min. Salmonella typhimurium was successfully detected with a limit of detection of 1000 CFU mL−1 from urine samples. The chip-based bacteria detection proposed in this study is a promising tool for sensitive, accurate, and multiplex identification of bacteria in clinical urine samples of UTIs and bacteriuria.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Coronavirus articles - free to access collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...