A nitrocellulose membrane-based integrated microfluidic system for bacterial detection utilizing magnetic-composite membrane microdevices and bacteria-specific aptamers†‡
Abstract
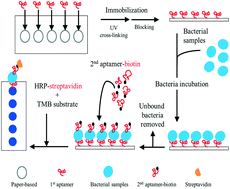
Bacteria such as Acinetobacter baumannii (AB) can cause serious infections, resulting in high mortality if not diagnosed early and treated properly; there is consequently a need for rapid and accurate detection of this bacterial species. Therefore, we developed a new, nitrocellulose-based microfluidic system featuring AB-specific aptamers capable of automating the bacterial detection process via the activity of microfluidic devices composed of magnetic-composite membranes. Electromagnets were used to actuate these microfluidic devices such that the entire diagnostic process could be conducted in the integrated microfluidic system within 40 minutes with a limit of detection as low as 450 CFU per reaction for AB. Aptamers were used to capture AB in complex samples on nitrocellulose membranes, and a simple colorimetric assay was used to estimate bacterial loads. Given the ease of use, portability, and sensitivity of this aptamer-based microfluidic system, it may hold great promise for point-of-care diagnostics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...