3D material cytometry (3DMaC): a very high-replicate, high-throughput analytical method using microfabricated, shape-specific, cell-material niches†
Abstract
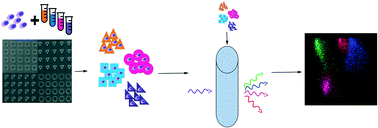
Studying cell behavior within 3D material niches is key to understanding cell biology in health and diseases, and developing biomaterials for regenerative medicine applications. Current approaches to studying these cell–material niches have low throughput and can only analyze a few replicates per experiment resulting in reduced measurement assurance and analytical power. Here, we report 3D material cytometry (3DMaC), a novel high-throughput method based on microfabricated, shape-specific 3D cell–material niches and imaging cytometry. 3DMaC achieves rapid and highly multiplexed analyses of very high replicate numbers (“n” of 104–106) of 3D biomaterial constructs. 3DMaC overcomes current limitations of low “n”, low-throughput, and “noisy” assays, to provide rapid and simultaneous analyses of potentially hundreds of parameters in 3D biomaterial cultures. The method is demonstrated here for a set of 85 000 events containing twelve distinct cell–biomaterial micro-niches along with robust, customized computational methods for high-throughput analytics with potentially unprecedented statistical power.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...