Thermo-acoustofluidic separation of vesicles based on cholesterol content†
Abstract
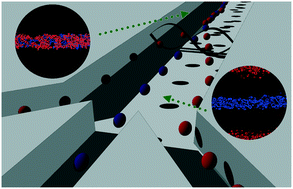
Biomechanical properties of cells such as cellular stiffness have been increasingly considered as biomarkers for diseases. For instance, stiffness of cancer cells has been correlated to the malignant potential in certain cell lines. In cells, the cholesterol content plays a crucial role in determining stiffness. Changes in the cholesterol content in cellular membranes can be an indication of pathological disorders. Acoustophoresis as a separation and diagnostic tool is well positioned to help in the separation and diagnosis of cells taking advantage of its unique separation criteria of density and compressibility. However, under the same conditions, cells and vesicles secreted by these cells often have a positive contrast factor sign and thus do not yield simple separations. Thermally-assisted acoustophoresis, also referred to as thermo-acoustophoresis, solves this problem by adding a temperature dimension to the separation. In this work, we evaluate the acoustic contrast temperature (TΦ) of vesicles at different cholesterol molar ratios (Xchol) and develop a multi-stage lab-on-a-chip method to accomplish for the first time the separation of a three-vesicle mixture. Using Xchol = 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3 vesicles, we have obtained separation efficiencies exceeding 93%. The simplicity, rapidity, and label-free nature of this approach holds promise as a diagnostic and separation tool for cells and extracellular vesicles such as exosomes and microvesicles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...