Phenotypic drug profiling in droplet microfluidics for better targeting of drug-resistant tumors†
Abstract
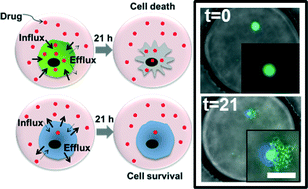
Acquired drug resistance is a key factor in the failure of chemotherapy. Due to intratumoral heterogeneity, cancer cells depict variations in intracellular drug uptake and efflux at the single cell level, which may not be detectable in bulk assays. In this study we present a droplet microfluidics-based approach to assess the dynamics of drug uptake, efflux and cytotoxicity in drug-sensitive and drug-resistant breast cancer cells. An integrated droplet generation and docking microarray was utilized to encapsulate single cells as well as homotypic cell aggregates. Drug-sensitive cells showed greater death in the presence or absence of Doxorubicin (Dox) compared to the drug-resistant cells. We observed heterogeneous Dox uptake in individual drug-sensitive cells while the drug-resistant cells showed uniformly low uptake and retention. Dox-resistant cells were classified into distinct subsets based on their efflux properties. Cells that showed longer retention of extracellular reagents also demonstrated maximal death. We further observed homotypic fusion of both cell types in droplets, which resulted in increased cell survival in the presence of high doses of Dox. Our results establish the applicability of this microfluidic platform for quantitative drug screening in single cells and multicellular interactions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanoengineering for Medicine and Biology (NEMB 2015)

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...