Microfluidic mixing of nonpolar liquids by contact charge electrophoresis†
Abstract
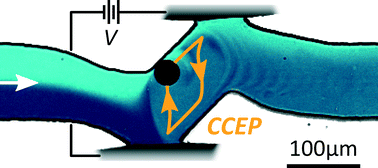
We present a simple and effective ratcheted microfluidic mixer that uses contact charge electrophoresis (CCEP) of a micron-scale particle to rapidly mix nonpolar liquids. CCEP combines contact charging and electrostatic actuation to drive the continuous oscillatory motion of a conductive particle between two electrodes subject to a constant (DC) voltage. We show how this oscillatory motion can be harnessed to mix laminar flows by using dielectric “ramps” to direct the particle along non-reciprocal, orbital trajectories, which repeatedly stretch and fold the flowing streams. Complete mixing requires that the speed of the particle is much larger than the fluid velocity such that the particle completes many orbits as the fluid flows through the mixing region. The extent of mixing also depends strongly on the size of the particle and the shape of its trajectory; effective mixers relied on larger particles (comparable to the size of the channel) moving along non-reciprocal orbits. While the present study uses mineral oil as a convenient nonpolar liquid, we also screened fifteen common solvents to determine the applicability of CCEP for mixing other organic liquids. Owing to its simple design and low power requirements (~100 nW), the orbital mixer presented here demonstrates the utility and versatility of ratcheted electrostatic actuation in powering active microfluidic operations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...