Integrated ionic liquid-based electrofluidic circuits for pressure sensing within polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic systems
Abstract
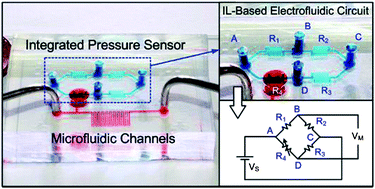
This paper reports a novel pressure sensor with an electrical readout based on electrofluidic circuits constructed by

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...