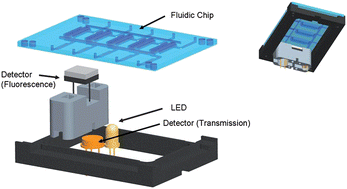
Coeliac disease is an inflammatory disease of the upper small intestine and results from gluten ingestion in genetically susceptible individuals, and is the only life-long nutrient-induced enteropathy. The only treatment is a strict gluten-free diet and the longer the individual fails to adhere to this diet, the greater the chance of developing malnutrition and other complications. The existence of reliable gluten free food is crucial to the well-being of the population. Here we report on a microfluorimeter device for the in situdetection of gliadin in foodstuffs, which could be used for a rapid control of raw materials in food processing, as well as for process control of gliadin contamination. The microfluorimeter is based on a reflector that is used inside a microfluidic chip, exploiting various strategically placed reflective or totally metallised mirrors for efficient collection of the fluorescent light emitted in a large solid angle. The chip is capable of executing five assays in parallel and has been demonstrated to possess detection sensitivity applicable to fluoroimmunoassays. Various immunoassay formats exploiting fluorescence detection, using enzyme/fluorophore labels were developed and compared in terms of sensitivity, ease of assay, assay time and compatibility with buffer used to extract gliadin from raw and cooked foodstuffs, with the best performance observed with an indirect competition assay using a fluorophore-labelled anti-mouse antibody. This assay was exploited within the microfluorimeter device, and a very low detection limit of 4.1 ng/mL was obtained. The system was observed to be highly reproducible, with an RSD of 5.9%, for a concentration of 50 ng/mL of gliadin applied to each of the five channels of the microfluorimeter. Biofunctionalised disposable strips incorporated into the microfluorimeter were subjected to accelerated Arrhenius thermal stability studies and it was demonstrated that strips pre-coated with gliadin could be stored for ≈ 2 years at 4 °C, with no discernable loss in sensitivity or detectability of the assay. Finally, the microfluorimeter was applied to the analysis of commercial gluten-free food samples, and an excellent correlation with routine ELISA measurements was obtained. The developed microfluorimeter should find widespread application for on-site execution of fluoroimmunoassays.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...