Microfluidic system with integrated electroosmotic pumps, concentration gradient generator and fish cell line (RTgill-W1)—towards water toxicity testing†
Abstract
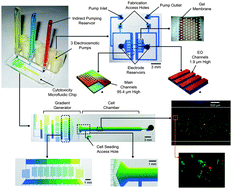
This study presents a microfluidic system that incorporates electroosmotic pumps, a concentration gradient generator and a fish cell line (rainbow trout gill) to perform toxicity testing on fish cells seeded in the system. The system consists of three mechanical components: (1) a toxicity testing chip containing a microfluidic gradient generator which creates a linear concentration distribution of toxicant in a cell test chamber, (2) an electroosmotic (EO) pump chip that controls the flow rate and operation of the toxicity chip, and (3) indirect reservoirs that connect the two chips allowing for the toxicant solution to be pumped separately from the electroosmotic pump solution. The flow rate and stability of the EO pumps was measured and tested by monitoring the gradient generator using

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...