Temporal analysis of protozoan lysis in a microfluidic device
Abstract
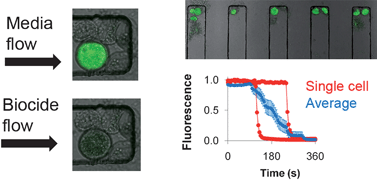
A microfluidic device was fabricated and characterized for studying cell lysis of Arcella vulgaris, a nonpathogenic amoeba, over time. The device contains a series of chambers which capture cells allowing them to be subsequently exposed to a constant flow of biocidal agent. With this microfluidic system, individual cells are observed as they undergo lysis. This allows high-throughput measurements of individual lysis events, which are not possible with conventional techniques. Differences in lysis and decay times for Arcella were seen at different flow rates and concentrations of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...