Generation of Janus alginate hydrogel particles with magnetic anisotropy for cell encapsulation†
Abstract
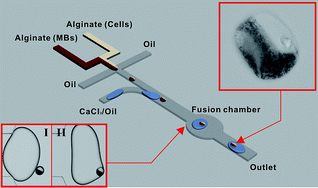
A microfluidic approach for fabrication of Janus hydrogel particles with magnetic anisotropy is demonstrated. Using this technique, cells and magnetic beads (MBs) can be separately embedded in one hydrogel particle to maintain optical performance, and reduce the contact between cells and magnetic beads (nano- or submicron-particles). Alginate cell capsules prepared by this method can be easily controlled and manipulated by external magnetic fields and require no specific surface modification. Bio-degradability and super-paramagnetic properties of these hydrogel particles were also demonstrated experimentally.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...