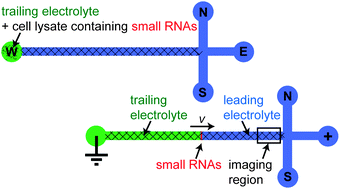
We present a technique which enables the separation of small RNAs—such as microRNAs (miRNAs), short interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs)—from ≥66 nucleotide RNAs and other biomolecules contained in a cell lysate. In particular, the method achieves separation of small RNAs from precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) in less than 3 min. We use on-chip isotachophoresis (ITP) for the simultaneous extraction, isolation, preconcentration and quantitation of small RNAs (∼22 nucleotides) and employ the high-efficiency sieving matrix Pluronic F-127; a thermo-responsive triblock copolymer which allows convenient microchannel loading at low temperature. We present the isolation of small RNAs from the lysate of 293A human kidney cells, and quantitate the number of short RNA molecules per cell to be 2.9 × 107. We estimate this quantity is an aggregate of roughly 500 types of short RNA molecules per 293A cell. Currently, the minimal cell number for small RNA extraction and detection with our method is ∼900 (from a 5 µL sample volume), and we believe that small RNA analysis from tens of cells is realizable. Techniques for rapid and sensitive extraction and isolation of small RNAs from cell lysate are much-needed to further uncover their full range and functionality, including RNA interference studies.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...