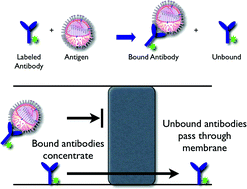
Towards developing rapid and portable diagnostics for detecting zoonotic diseases, we have developed microchip-based electrophoretic immunoassays for sensitive and rapid detection of viruses. Two types of microchip-based electrophoretic immunoassays were developed. The initial assay used open channel electrophoresis and laser-induced fluorescence detection with a labeled antibody to detect influenza virus. However, this assay did not have adequate sensitivity to detect viruses at relevant concentrations for diagnostic applications. Hence, a novel assay was developed that allows simultaneous concentration and detection of viruses using a microfluidic chip with an integrated nanoporous membrane. The size-exclusion properties of the in situ polymerized polyacrylamide membrane are exploited to simultaneously concentrate viral particles and separate the virus/fluorescent antibody complex from the unbound antibody. The assay is performed in two simple steps—addition of fluorescently labeled antibodies to the sample, followed by concentration of antibody–virus complexes on a porous membrane. Excess antibodies are removed by electrophoresis through the membrane and the complex is then detected downstream of the membrane. This new assay detected inactivated swine influenza virus at a concentration four times lower than that of the open-channel electrophoresis assay. The total assay time, including device regeneration, is six minutes and requires <50 μl of sample. The filtration effect of the polymer membrane eliminates the need for washing, commonly required with surface-based immunoassays, increasing the speed of the assay. This assay is intended to form the core of a portable device for the diagnosis of high-consequence animal pathogens such as foot-and-mouth disease. The electrophoretic immunoassay format is rapid and simple while providing the necessary sensitivity for diagnosis of the illness state. This would allow the development of a portable, cost-effective, on-site diagnostic system for rapid screening of large populations of livestock, including sheep, pigs, cattle, and potentially birds.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...