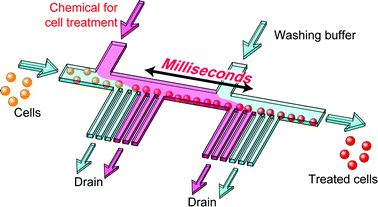
We present herein a simple but versatile microfluidic system for the treatment of cells with millisecond chemical stimulus, by rapidly exchanging the carrier-medium of cells twice in a microchannel. A technique we refer to as ‘hydrodynamic filtration’ has been employed for the exchange of medium, in which the virtual width of flow in the microchannel determines the size of filtered cells/particles. The treatment time of cells could be rigidly adjusted by controlling the inlet flow rates and by changing the volume of the stimulating area in the microchannel. In the experiment, two types of microdevices were designed and fabricated, and at first, the ability for carrier-medium exchange was confirmed. As an application of the presented system, we examined the influence of the treatment time of HeLa cells with Triton X-100, a non-ionic surfactant used to solubilize the cellular membrane, on cell viability, varying the average treatment time from 17 to 210 ms. Both quantitative and qualitative analyses were performed to estimate the damage on cell membrane, demonstrating that the cell viability dramatically decreased when the treatment time was longer than ∼40 ms. The obtained results demonstrated the ability of the presented system to conduct the rapid stimulation of cells, which would be useful for the analysis of biochemical reactions at the cell surface.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...