The effect of photomask resolution on separation efficiency on microfabricated devices
Abstract
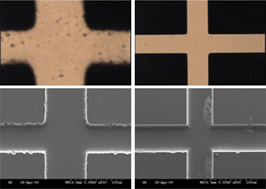
Separation quality on glass microfluidic devices fabricated from photomasks of different optical resolutions was compared by measuring the dispersion (apparent diffusion) coefficients of a set of standard compounds separated on these devices. Currently, the channel manifolds of most microfluidic devices are patterned using chrome photomasks. A much cheaper, more robust alternative to chrome photomasks are laser photoplotted masks. The primary disadvantage to using laser photoplots is that the optical resolution of these masks is not as high as that of chrome masks, and this feature increases the side-wall roughness of etched channel manifolds patterned using such masks. The increased wall roughness may affect the fluid flow within the channels and, therefore, the separation quality. To determine the effect of increased sidewall channel roughness, microchip channel manifolds were patterned in soda lime glass using a chrome photomask and laser photoplots printed at resolutions of 620, 1240, 3100 and 6200 dots per centimetre (dpc). Separations were performed on these devices using dilute solutions of fluorescently labeled amino acids. The peak variances of the amino acids were calculated at increasing distances down the separation channel and plotted as a function of migration time. From this plot, dispersion coefficients of the analytes were measured. This allowed for a reliable, relatively easy, direct separation analysis among microchips fabricated from the various photomasks. After multiple separations using microchips fabricated from each resolution mask, we found that the change in sidewall surface roughness did not significantly affect the dispersion coefficients measured, and thus the separation quality. The lower mask resolution limit, rather, was governed by the fidelity to which the mask could capture the original CAD design.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...