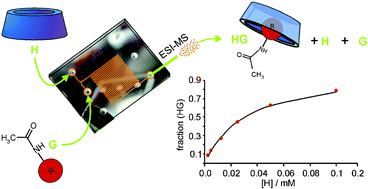
Two simple interfaces were designed and realized, enabling on-line coupling of microfluidics reactor chips to a nanoflow electrospray ionization (NESI) time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometer (MS). The interfaces are based on two different approaches: a monolithically integrated design, in which ionization is assisted by on-chip gas nebulization, and a modular approach implying the use of commercially available Picospray™ tips. Using reserpine as a reference compound in a 1∶1 mixture of acetonitrile and water revealed that both interfaces provide a remarkably stable mass spectrometric signal (standard deviations lower than 8% and 1% for the monolithic and modular approaches, respectively). Glass microreactors, containing mixing zones, were fabricated and coupled to the modular interface with perfluoroelastomer Nanoport™ fluidics connectors, providing a tool to study chemical reactions on-line. Investigation of the mixing dynamics showed that complete on-chip reagents mixing is achieved within a few tens of milliseconds. Metal–ligand interactions of Zn-porphyrin 1 with pyridine (2), 4-ethylpyridine (3), 4-phenylpyridine (4), N-methylimidazole (5), and N-butylimidazole (6) in acetonitrile as well as host–guest complexations of β-cyclodextrin (7) with N-(1-adamantyl)acetamide (8) or 4-tert-butylacetanilide (9) in water were studied by mass spectrometry using the modular NESI-chip interface. From on-chip dilution-based mass spectrometric titrations of Zn-porphyrin 1 with pyridine (2) or 4-phenylpyridine (4) in acetonitrile Ka-values of 4.6 ± 0.4 × 103 M−1 and 6.5 ± 1.2 × 103 M−1, respectively, were calculated. The Ka-values are about four times larger than those obtained with UV/vis spectroscopy in solution, probably due to a higher ionization efficiency of complexed compared to uncomplexed Zn-porphyrin. For the complexation of N-(1-adamantyl)acetamide (8) with β-cyclodextrin (7), a Ka-value of 3.6 ± 0.3 × 104 M−1 was obtained, which is in good agreement with that determined by microcalorimetry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...