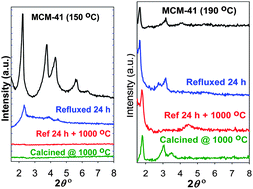
The influence of high temperature synthesis of MCM-41 on structural ordering, textural properties and stability has been investigated. Increasing the crystallization temperature resulted in the enlargement of pore size and some reduction of long-range ordering but at the same time generated thicker pore walls. The overall effect was a gradual decrease in surface area and pore volume accompanied by improvement in stability for higher crystallisation temperature samples. Successful synthesis of well ordered MCM-41 materials was achieved up to 190 °C, which is the highest temperature so far reported for synthesis of alkylammonium ion (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, CTAB) templated materials. MCM-41 samples synthesized at 180 and 190 °C exhibit thick (up to ca. 23 Å) pore walls wherein the silica is highly condensed and have much higher stability compared to a sample prepared at 150 °C. The sample prepared at 190 °C shows exceptional hydrothermal and thermal stability, even retaining long-range mesostructural ordering after refluxing in boiling water for 24 h or heating at 1000 °C for 4 h, which is unprecedented for pure silica MCM-41 materials. Rather unusually, we observed that the porosity of calcined high temperature pure silica MCM-41 samples may be further modified by refluxing in water. Refluxing of the calcined samples not only increased their porosity (surface area and pore volume) but, remarkably, also stabilised them to subsequent high temperature calcination at 1000 °C.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...