Osteoconductive surfaces generated from peptide functionalized poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl phosphate) brushes†‡
Abstract
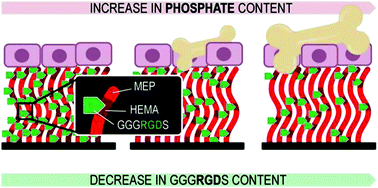
Modification of bone implant materials with biofunctional surfaces that facilitate osteoblast adhesion and promote matrix mineralization is an attractive strategy to improve osseointegration. This manuscript discusses the preparation and properties of RGD peptide modified poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl phosphate) (P(HEMA-co-MEP)) brushes. Whereas the RGD peptide serves to mediate osteoblast adhesion, the MEP phosphate groups were incorporated to mimic the function of natural bone extracellular matrix phosphorylated proteins and stabilize the bone mineral phase. The polymer brush coatings were obtained via surface-initiated atom transfer radical copolymerization of HEMA and MEP followed by peptide post-polymerization modification. The functional properties of these polymer brushes were evaluated in vitro using MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblast cells. Whereas cell proliferation and differentiation were not significantly influenced by variations in brush composition (MEP, peptide content), incorporation of MEP was found to promote matrix mineralization. Matrix mineralization was most pronounced on substrates that presented both phosphate groups and RGD peptide sequences, indicating that a simultaneous presentation of both of these cues is most favorable.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Materials for biosurfaces

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...