Li4P2O7 modified high performance Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode material
Abstract
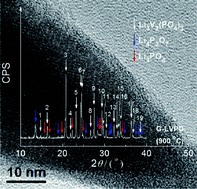
Li3V2(PO4)3 was prepared from a stoichiometric and a non-stoichiometric set of precursors. The non-stoichiometric preparation led to particles coated with a thin layer (<5 nm) of Li4P2O7 and Li3PO4 (G-LVPO), as verified through

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...