Probing the molecular structure of antimicrobial peptide-mediated silica condensation using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy†
Abstract
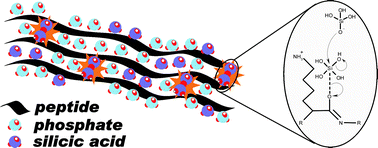
The antimicrobial peptide KSL (KKVVFKVKFK) mediates the rapid condensation of tetramethyl orthosilicate to form silica nanoparticles. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was employed to identify the molecular interactions between protein and silica on the surface of nanoparticles containing antimicrobial peptide and silica. Comparative high resolution spectral analysis between KSL peptide and KSL-catalyzed silica nanoparticles revealed that imidates are present in the KSL peptide backbone after silica formation. Supporting evidence for the presence of an imidate is provided by FTIR spectroscopic analysis of the amide I and V bands. XPS analysis also shows that side-chain amines of lysine do not interact with the silica product and the lack of association is supported further by 15N-29Si REDOR NMR. Quantitative analysis of XPS elemental spectra determined the silica O:Si ratio is 3.6 : 1, suggesting that the nuclei (sol) particles are not highly condensed structures. Results were supported using 29Si CPMAS NMR to show that the majority of the silica is Q2 groups. A proposed mechanism of rapid silicification with involvement of a peptide imidate is presented.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...