Photoluminescence investigations on a novel green-emitting phosphor Ba3Sc(BO3)3:Tb3+ using synchrotron vacuum ultraviolet radiation
Abstract
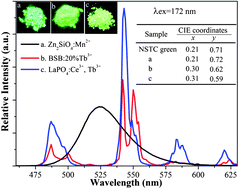
Vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) spectroscopic properties of undoped and Tb3+-doped Ba3Sc(BO3)3 were investigated by using synchrotron radiation. The Tb3+-doped Ba3Sc(BO3)3 sample crystallized in a flower-like shape even was synthesized at 1100 °C. Upon VUV excitation, Ba3Sc(BO3)3 exhibited an intrinsic broad UV emission centered at 336 nm, which results from radiative annihilation of self-trapped exciton (STE) that may presumably be associated with band-gap excitations or molecular transitions within the BO33− group. The maximum host absorption for Ba3Sc(BO3)3 was found at about 180 nm. Upon doping of Tb3+ ions into Ba3Sc(BO3)3, an efficient energy transfer from the host excitations to Tb3+via STE emission was observed, showing host sensitization of Tb3+ occurs. The energy transfer from host to Tb3+via STE emission in Ba3Sc(BO3)3:Tb3+ was studied as a function of temperature and Tb3+ doping concentration. It has been demonstrated that the energy transfer efficiency was increased with either increasing temperature or Tb3+ doping concentration. In the case of temperature dependent energy transfer, the energy transfer from the STE to Tb3+ is thermally activated, probably due to exciton mobility, while in the case of concentration dependent energy transfer, the energy transfer from the STE to Tb3+ is promoted due to a closer distance between the STE and Tb3+ at high Tb3+ concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...