Metal–organic frameworks for visible light absorption via anion substitution
Abstract
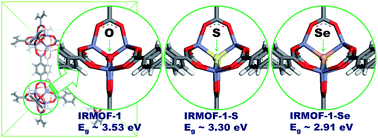
We report that the band gap of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) could be tuned to absorb visible light via anion substitution. First of all, when an oxygen anion in the metal
- This article is part of the themed collection: Integrating functionality into metal–organic frameworks

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...