Copper oxide activation of soft-templated mesoporous carbons and their electrochemical properties for capacitors†
Abstract
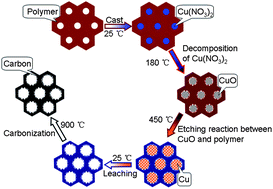
Ordered mesoporous carbon with a 2-D hexagonal mesostructure was prepared by an organic–organic co-assembly method. The mesoporous carbon was activated by using CuO to improve its mesoporosity. Compared with pristine mesoporous carbon (PMC-900) carbonized at 900 °C, the mean mesopore size of the activated mesoporous carbon (AMC-900) is increased from 3.2 to 5.5 nm by an etching reaction between copper oxide and the inner layer of the carbonaceous mesochannels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...