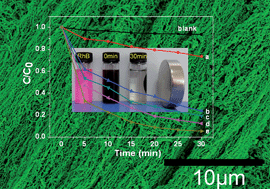
Magnetic-field induced formation of 1D Fe3O4/C/CdS coaxial nanochains as highly efficient and reusable photocatalysts for water treatment†
Abstract
We report a novel strategy for fabrication of one-dimensional (1D) Fe3O4/C/CdS coaxial nanochains via a magnetic field-induced

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...