Unsymmetric main-chain liquid crystal elastomers with tunable phase behaviour: elastic response†
Abstract
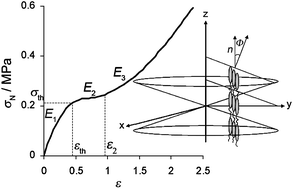
In this paper are reported the results of an investigation of the mechanical and thermoelastic properties of a new series of polysiloxane-based MC-LCEs containing different unsymmetric mesogenic units, siloxane spacers and cross-linkers. The structure of the networks has been varied systematically in order to study their properties. The mechanical properties of polydomain and monodomain elastomers were characterised by stress and strain measurements. The mechanical behaviour of the elastomer networks can be divided into two groups according to the phases they presented. Elastomers that contained flexible cross-linker, C1, and showed a SmC phase, demonstrated a non-linear elastic response when stress was applied in the axis of the domain director, in contrast to earlier experiments. In the axis normal to the director, at low strains, the response was linear and the Young's modulus was ten times lower compared to that in the axis of the director, demonstrating the marked anisotropic nature of these systems. The elastomers containing cross-linker C2 were nematic and showed lower Young's moduli compared to the smectic systems. The thermoelastic response of these systems showed spontaneous elongations up to 88% of strain when the samples were cooled from the isotropic to the liquid crystal phase, supporting stresses of 120 kPa. The properties are discussed in terms of the chemical structure of the networks in order to establish a correlation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Mechanoresponsive materials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...