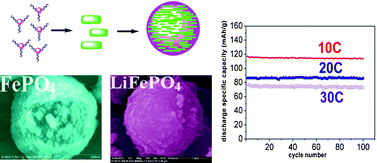
LiFePO4/C microspheres composed of many densely compact nanoplates were synthesized by a simple rheological phase method using nanoplate assembled quasi-microspheres of FePO4·2H2O as raw materials. The quasi-sphere FePO4·2H2O precursors were synthesized via a sodium dodecylsulfate assisted hydrothermal process. Both the LiFePO4/C composite and the FePO4·2H2O precursors were characterized by XRD, TG, SEM, TEM, and Raman spectroscopy. The FePO4·2H2O quasi-spheres had a size distribution of about 1 μm and were composed of nanoplates with a 30 nm thickness. The LiFePO4/C microspheres were also composed of the same sized nanoplates with an ∼2 nm thick amorphous carbon layer coating at the surface. The as-synthesized LiFePO4/C composite showed excellent high-rate capability, with discharge capacities reaching 116, 96 and 75 mAh g−1 at 10 C, 20 C and 30 C current rates, respectively. Furthermore, the LiFePO4/C material composed of microspheres had a high tap density (1.4 g cm−3). Therefore, this LiFePO4/C material can be the cathode material for large-scale applications such as electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...