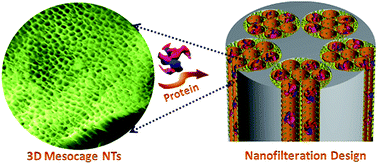
Large three-dimensional (3D) mesocage structures that have multidirectional pore networks and uniform openings perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of NTs are of particular interest in terms of their potential. This paper reports on the feasibility of direct control of 3D mesopore cage structures throughout silica nanotubes (NTs) vertically aligned inside Anodic Alumina Membrane (AAM) nanochannels without the use of any organic stabilizing modifiers. This is the first reported study which uses direct synthesis of ordered cubic Im3m mesocage structures inside well-aligned silica-NTs that have open surfaces of top-bottom ends, and multidirectional (3D) mesopore connectivity. These 3D mesocage silica-NT arrays hybrid AAM channels function as nanofilters that can rapidly (in seconds) separate large quantities of proteins. In this nanofiltration assay, three proteins that differ in molecular weight and size such as cytochrome c (CytC), myoglobin (Mb), and hemoglobin (Hb) were used. The prominent factors affecting nanofiltration and permeation flux performance of nanoscale cage membranes are: (i) the concentration of the feed solution of protein (retentate), (ii) molecular sizes and weights of proteins, and (iii) stability of the hierarchical mesocage structures during the filtration and permeation processes. Although the protein nanofiltration efficiency decreased during the reuse cycles of the nanofilter membranes, the proposed nanofilters still exhibited well-controlled molecular-size cut-off after a number of cycles. These mesocage silica-NT-supported membranes are expected to be promising for the development of new generation high-precision, uniform-porosity, and bio-compatible nanofilters with molecular-size cut-off systems.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...