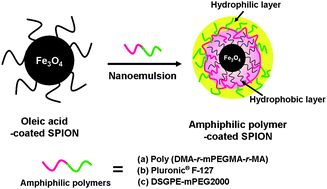
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) are widely used as T2-contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Herein we develop various antibiofouling amphiphilic polymer-coated SPIONs using a one-step nanoemulsion method. This methodology yielded ultrasmall polymer-coated SPIONs, of average diameter less than 30 nm, which were stable under physiological conditions. In vitrocell cytotoxicity tests revealed that no SPION showed toxicity even at relatively high concentrations. In vivo MRI with Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) tumor-bearing mice resulted in an approximately 30% T2 signal drop in tumor tissues, indicating that the SPIONs reached such tissues via passive targeting. In summary, the ultrasmall, stable, amphiphilic polymer-coated SPIONs can be used as MRI contrast agents for cancer imaging.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...