Preparation of graphitic carbon with high surface area and its application as an electrode material for fuel cells
Abstract
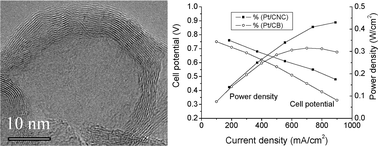
Nanostructured graphitic carbon materials have wide applications. However, the synthesis of such materials with a high surface area is still a great challenge. In this study, graphitic carbon

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...