Cobalt speciation in cobalt oxide-apatite materials: structure–properties relationship in catalytic oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane and butan-2-ol conversion
Abstract
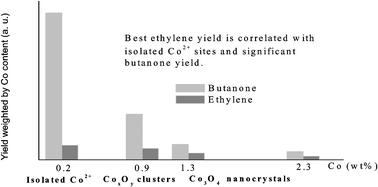
Impregnation of calcium hydroxyapatite by a solution of Co(II) nitrate followed by calcination at 823 K gives rise to various species, depending on the cobalt content. At low cobalt content (0.2 wt%), the cobalt species are isolated six-coordinated Co2+ ions. For Co content ≥0.4 wt%, the presence of tetrahedral Co2+ and octahedral Co3+ species is attested by UV–visible–NIR spectroscopy, magnetic measurements and XPS data. Magnetic data at low temperature suggest the formation of clustered CoxOy entities. For Co content ≥1.7 wt%, Co3O4 nanocrystals are generated, as evidenced by XRD and magnetic measurements.
In the presence of oxygen, the butan-2-ol conversion produces only butan-2-one. The most active catalysts are the cobalt poorest samples which contain only isolated Co2+ ions. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane gives a similar trend. Upon increasing the cobalt loading above 0.9 wt%, the specific dehydrogenation activity of Co2+ ions decreases because the nature of the sites changes and the basic properties are lowered. Relationships between the nature of the sites and the catalytic performances are proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...