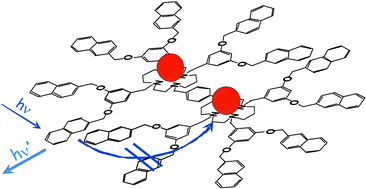
We have synthesized a novel dendrimer (1) based on two covalently linked cyclam units as a core appended to six branches, each one consisting of one dimethoxybenzene and two naphthyl units (cyclam = 1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane). Such a dendrimer shows three fluorescence bands which can be assigned to naphthyl localized excited states (λmax
= 336 nm), naphthyl excimers (λmaxca. 390 nm), and naphthyl–amine exciplexes (λmax
= 510 nm). Protonation or complexation of the bis-cyclam core with Zn2+ does not affect the absorption spectrum of the dendrimer, but causes noticeable changes in the fluorescence intensity of the three component bands. Complexation with Cu2+ not only causes changes in the relative intensities of the fluorescence bands, but also the appearance of a new absorption band in the near UV spectral region. Analysis of the titration curves has allowed us to obtain clear evidence for the formation of 1 : 1 (1(H+), [Zn(1)]2+, [Cu(1)]2+) and 2 : 1 (1(2H+), [Zn2(1)]4+, [Cu2(1)]4+) species. Comparison with the behaviour of a previously investigated parent monocyclam dendrimer (2) suggests that in the 1 : 1 species of 1 both the cyclam units are involved in the complexation with Zn2+ and Cu2+.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...