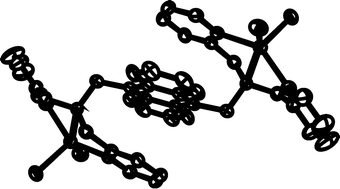
Anthracene derivatives (1, 2) having one or two diethylamine (a), N-methyl-piperazine (b) and N,N-bis(2-dipicolyl)amine units (c) showed weak emission, suggesting that photoinduced electron transfer (PET) from the amine group to the excited anthracene occurs. The PET fluoroionophores (1, 2) were found to display unique photophysical properties in the presence of the guest metal salts. Complexation of diethylamine (1a, 2a) and N-methyl-piperazine derivatives (1b, 2b) with Ni2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ enhanced the emission, while the emission intensities of N,N-bis(2-picolyl)amine derivatives (1c, 2c) are increased in the presence of Zn2+ and decreased in the presence of Ni2+ and Cu2+. The crystal structures of 2c and its zinc chloride complex showed that the binding of Zn2+ to the N,N-bis(2-picolyl)aminomethyl unit inhibits the photoinduced electron transfer process. Intramolecular π–π interactions between anthracene and the ZnCl2-complexed pyridine were observed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...