Ultra-trace determination of thallium by electrochemical hydride generation using efficient tungsten electrodes followed by in situ trapping on a graphite tube and detection by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry†
Abstract
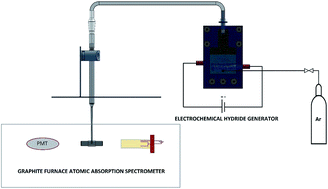
A novel and extremely efficient cathode material, namely, tungsten-inert gas welding electrode, along with Pd(II) as an enhancement reagent has been introduced for electrochemical hydride generation of thallium (Tl). In situ trapping of the volatile species on a graphite tube along with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry was used for preconcentration and detection of Tl in order to provide high sensitivity. The volatile species were transferred to the graphite tube by the flow of argon gas and trapped there for a time period of 170 s. To optimize the performance of the proposed analytical method, effects of several effective experimental parameters, such as the graphite tube modifier, argon gas flow rate, trapping temperature and period, atomization temperature, concentration of the catholyte, and also electrolysis duration were investigated and discussed. Under optimum operating conditions, the calibration curve was plotted which was linear in the concentration range of 28 to 300 ng L−1 of Tl. The limit of detection (LOD) and the limit of quantification (LOQ) of the method were obtained to be 8 ng L−1 and 28 ng L−1, based on 3sb/m and 10sb/m criteria, respectively. The relative standard deviation (RSD%) of the method was found to be 2% for seven replicate measurements at a concentration level of 150 ng L−1 of Tl. The effects of several potential chemical interferents were studied and discussed. The accuracy and the analytical applicability of the proposed method were checked through the analysis of commercial certified reference materials, namely, contaminated unalloyed zinc (ERM®-EB325) and also drinking water containing trace metals (CRM-TMDW). As this method was insensitive towards the oxidation state of Tl, it is suitable for the determination of the total Tl in real analytical samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...