Improved in situ Li isotopic ratio analysis of silicates by optimizing signal intensity, isotopic ratio stability and intensity matching using ns-LA-MC-ICP-MS
Abstract
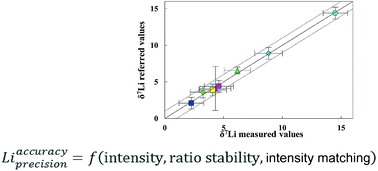
In order to obtain the accurate and precise in situ Li isotopic composition of silicate samples by LA-MC-ICP-MS (Thermo Neptune Plus), high sensitivity (signal/background ratio), stable isotopic ratio measurement and a reduced intensity mismatch effect are necessary. The effects of two cone combinations, the distance between the sample cone and the end of the torch, i.e., the sampling depth, sample gas flow rate and intensity mismatch of the samples and standard on the determination of Li isotopic ratios were investigated. Compared to the Jet + X cone combination, the signal/background ratio was enhanced by a factor of 4–6 with the use of standard + X. A higher sample gas flow rate and shallower sampling depth are recommended to stabilize the 7Li/6Li ratio. The effect of intensity mismatch was reduced by adjusting the intensity difference between the samples and standard within 40% by using different laser repetition rates. Applying the optimized method, the measured Li isotope ratios for USGS (BHVO-2G) and MPI-DING glasses (KL2-G, ML3B-G, StHs6/80-G, GOR128-G, GOR132-G, ATHO-G and T1-G) are in good agreement with the recommended values within their uncertainties, demonstrating that appropriate optimization of the operating parameters of 193 nm excimer LA-MC-ICP-MS is beneficial to obtain accurate Li isotopic analysis of geological samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...