Calibration of Mo isotope amount ratio measurements by MC-ICPMS using normalisation to an internal standard and improved experimental design†
Abstract
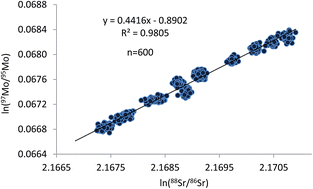
Improved methodology for high accuracy Mo isotope amount ratio measurements by multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (MC-ICPMS) using normalisation to an internal standard is presented. It is based on the use of the regression model to correct for instrumental mass discrimination with NIST Standard Reference Material 987, certified for Sr isotope ratios, as the internal standard. Calibration factors for measured Mo isotope ratios were calculated from calibration factors for Sr isotope ratios by using an experimentally established relationship between variations in simultaneously measured Mo and Sr isotope ratios. The novelty of the developed methodology lies in the use of controlled changes in the magnitude of instrumental mass discrimination, achieved by small incremental changes in RF power of the plasma in the measurements, in order to better define a relationship between isotope ratios of the analyte and internal standard. The Mo isotope amount ratios with associated expanded uncertainties (k = 2), as determined for an in-house standard, a high-purity Mo metal rod from Johnson Matthey, were as follows: 92Mo/95Mo = 0.9223(15), 94Mo/95Mo = 0.5790(3), 96Mo/95Mo = 1.0500(6), 97Mo/95Mo = 0.06028(9), 98Mo/95Mo = 1.5278(30), 100Mo/95Mo = 0.6124(25). These values are in excellent agreement with those obtained previously for the same standard using calibration with synthetic isotope mixtures. Overall, the measurement uncertainties obtained by the two calibration approaches are fairly comparable. Performance of the regression model with the improved measurement strategy, in terms of accuracy and precision of Mo isotope amount ratios, was shown to be superior to that of other available models to correct for instrumental mass bias, including the linear, exponential and power models. For the first time in MC-ICPMS, a test of ruggedness of Mo isotope ratio measurements with normalisation to internal standard was performed using a Plackett–Burman factorial design. Full uncertainty budgets for the measurements are presented and identification of the major sources of uncertainty is provided. The developed methodology has been demonstrated to be a promising tool for certification of reference materials for isotopic measurements by offering an independent and less expensive calibration method to the one based on the use of synthetic isotope mixtures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...