Comparison of 795 nm and 265 nm femtosecond and 193 nm nanosecond laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for the quantitative multi-element analysis of glass materials
Abstract
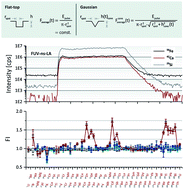
The figures of merit of femto- and nanosecond laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry applying near infrared, middle ultraviolet, and far ultraviolet radiation at 795 nm, 265 nm, and 193 nm, respectively, for the quantitative multi-element analysis of glass materials were compared. Major, minor, and trace elements of four glass reference materials including NIST612, BCR-2G, GSE-1G, and BAM-S005A were quantified against NIST610 applying Ca or Si as an internal standard. Deviations between measured element concentrations and literature values were compared and it was demonstrated that all systems provide similar results when using Ca as an internal standard. By contrast, concentrations obtained by femtosecond laser ablation at 795 nm with Si as an internal standard showed deviations by up to 20% under the operating conditions chosen. Furthermore, Si-normalized fractionation indices calculated for nanosecond laser ablation at 193 nm as well as femtosecond laser ablation at 795 nm and 265 nm suggested these discrepancies to be, on the one hand, due to changes in the composition and/or particle size distribution of aerosols formed over the sampling time. On the other hand, Ca-normalized fractionation plots for femtosecond laser ablation at 795 nm turned out to be less informative with respect to quantification accuracy and, in addition, questioned their general significance. An adaptation of instrumental parameters was found to result in fractionation indices closer to unity signifying that both fluence and spot size are crucial parameters, controlling compositions and/or particle size distributions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Geological applications of laser ablation

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...