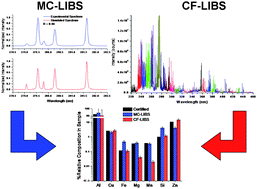
Two standard free approaches to the quantitative analysis of aluminum alloys by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) are compared—the calibration-free LIBS (CF-LIBS) approach and the Monte Carlo simulated annealing optimization method (MC-LIBS). The experiments are carried out under a pressure of 0.1 mbar, using a Nd-YAG at 1064 nm, with a 5.3 ns nominal pulse width, an energy of 90 mJ/pulse and a spot size on the target of 0.070 cm, resulting in an irradiance of 4.4 GW/cm2. The spectra are taken with a grating monochromator calibrated over a wide spectral range and equipped with an intensified CCD detector. A gate width of 100 ns has been chosen for the measurements. In the MC model, a direct-inverse approach is used, where simulated and experimental spectra are correlated with each other until a satisfactory correlation coefficient is obtained. Spatially resolved measurements are also performed, by recording the plasma emission in the imaging mode and binning the resulting image into 11 different spatial positions along the axial direction, each binned region being equivalent to ∼ 0.025 cm portion of the vertical plasma partition. The spectrum obtained for each spatial position is still spatially integrated along the line-of-sight. Comparatively, concentration values obtained with CF-LIBS for the matrix element Al are much closer to the certified values than those obtained with MC-LIBS (4% versus 20% relative errors, respectively), while the relative concentration obtained for the remainder of the sample components resulted in relative errors that are comparable in magnitude with both approaches (30%–250% relative errors). It is argued that the necessity of improving the space and time resolution of the experimental set-up appears to be at least as important as that of refining the theoretical models.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...