Measurement of the microdistribution of strontium and lead in bone via benchtop monochromatic microbeam X-ray fluorescence with a low power source†
Abstract
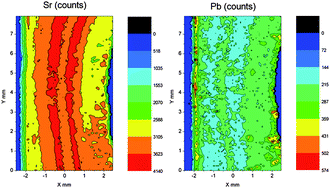
Determination of the microdistribution of trace elements in bone at low concentrations has previously been performed with

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...